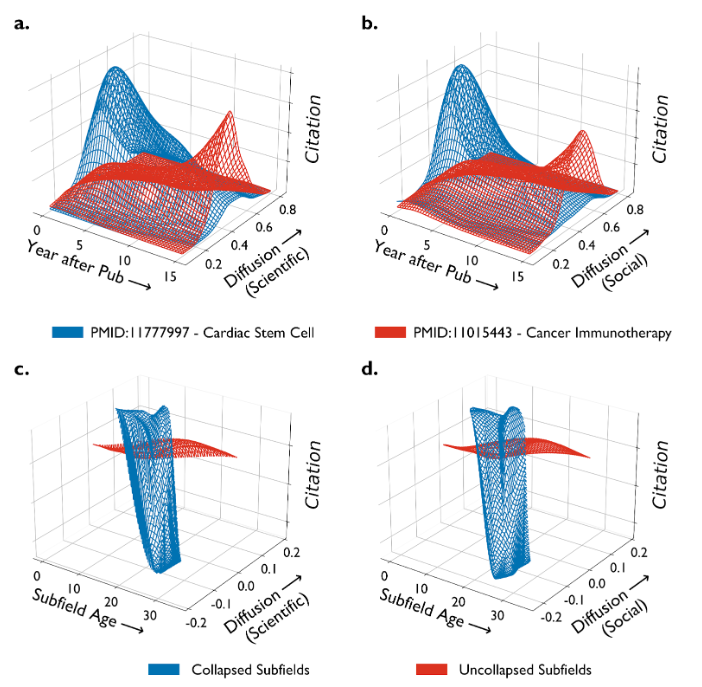
Limited Diffusion of Scientific Knowledge Forecasts Collapse
Kang, Donghyun, Robert S. Danziger, Jalees Rehman, and James A. Evans, Nature Human Behaviour (2024) https://www.nature.com/articles/s41562-024-02041-0
Abstract: Market bubbles emerge when asset prices are driven unsustainably higher than asset values, and shifts in belief burst them. We demonstrate an analogous phenomenon in the case of biomedical knowledge, when promising research receives inflated attention. We introduce a diffusion index that quantifies whether research areas have been amplified within social and scientific bubbles, or have diffused and become evaluated more broadly. We illustrate the utility of our diffusion approach in tracking the trajectories of cardiac stem cell research (a bubble that collapsed) and cancer immunotherapy (which showed sustained growth). We then trace the diffusion of 28,504 subfields in biomedicine comprising nearly 1.9 M papers and more than 80 M citations to demonstrate that limited diffusion of biomedical knowledge anticipates abrupt decreases in popularity. Our analysis emphasizes that restricted diffusion, implying a socio-epistemic bubble, leads to dramatic collapses in relevance and attention accorded to scientific knowledge.
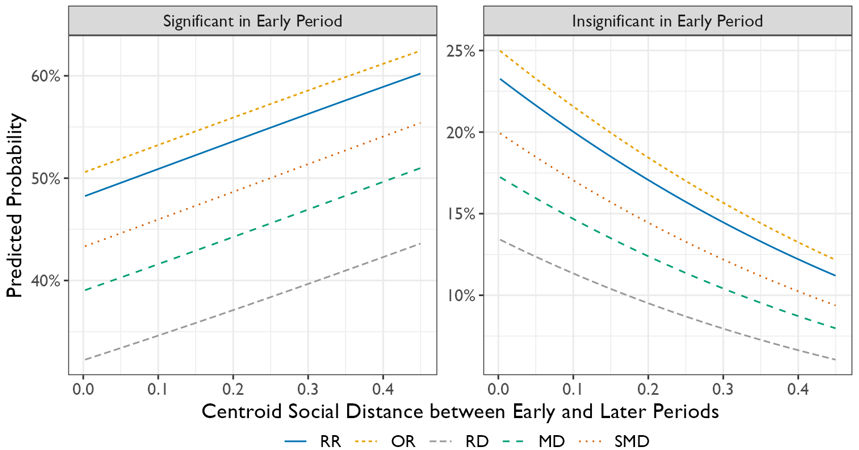
Socio-Epistemic Bubbles and Tacit Confidence in Randomized Clinical Trials
Kang, Donghyun and James A. Evans, Under Review, Preprint
Abstract: The paradigm of scientific medicine is among the most influential epistemic shifts in the past century, wherein randomized clinical trials (RCTs) represent the impartial arbiter of legitimate medical knowledge, a view prevalent among quantitative social scientists. Nevertheless, not all RCTs agree, and systematic reviews are invoked to reconcile them. These assume the wisdom of crowds, which hinges on diverse perspectives and data, across the distribution of analyzed studies, but socio-epistemic bubbles across them may reduce realized diversity. We theorize how tacit knowledge, beliefs, and expectations accumulate within these ‘socio-epistemic bubbles,’ continuous regions of latent social density that may decrease diversity and increase certainty about healthcare studied by RCTs. To assess our theory, we analyze the Cochrane systematic review repository, covering 20,117 meta-analyses extracted from 1,962 reviews. We find that being closer within ‘social space’ inscribed by scientific collaboration markedly increases agreement regarding RCT effect direction and size. Our analysis suggests that this amplified certainty can drive premature convergence and path-dependency affecting medical practice and population health. Moreover, our findings imply hidden limitations associated with unmeasured social influence across the policy sciences through which conflicting claims perpetuate and highlight the necessity of accounting for them to improve collective certainty.
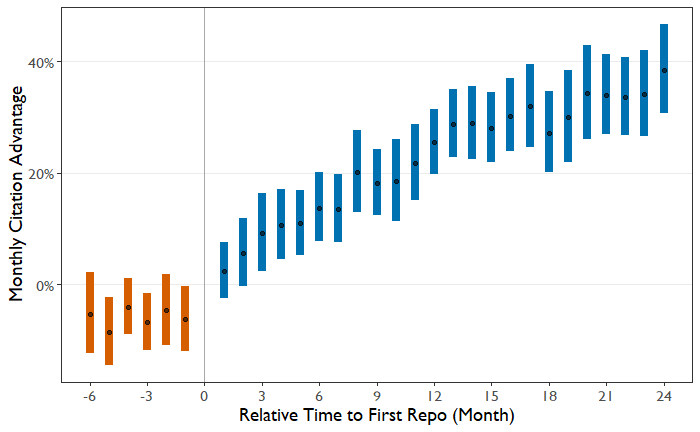
Papers with code or without code? Impact of GitHub repository usability on the diffusion of machine learning research
Kang, Donghyun, TaeYoung Kang, and Junkyu Jang. Information Processing & Management 60, no. 6 (2023): 103477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2023.103477
Abstract: Open Science initiatives prompt machine learning (ML) researchers and experts to share source codes - “scientific artifacts” - alongside research papers via public repositories such as GitHub. Here we analyze the extent to which 1) the availability of GitHub repositories influences paper citation and 2) the popularity trend of ML frameworks (e.g., PyTorch and TensorFlow) affects article citation rates. To accomplish this, we connect ML research publications indexed by Papers with Code (PwC) to Microsoft Academic Graph (MAG) and collect repository-level metadata using the GitHub API. Applying nearest-neighbor matching and econometric considerations, we estimate that papers enjoy approximately 20% advantages in monthly citation rates after the creation of the first GitHub repositories, accounting for paper-level fixed effects and ages. We also find that the temporal popularity trends for frameworks used in the first associated repositories could influence the monthly citation rate for papers. The results highlight the importance of technological artifacts and infrastructure latent to the diffusion of research.
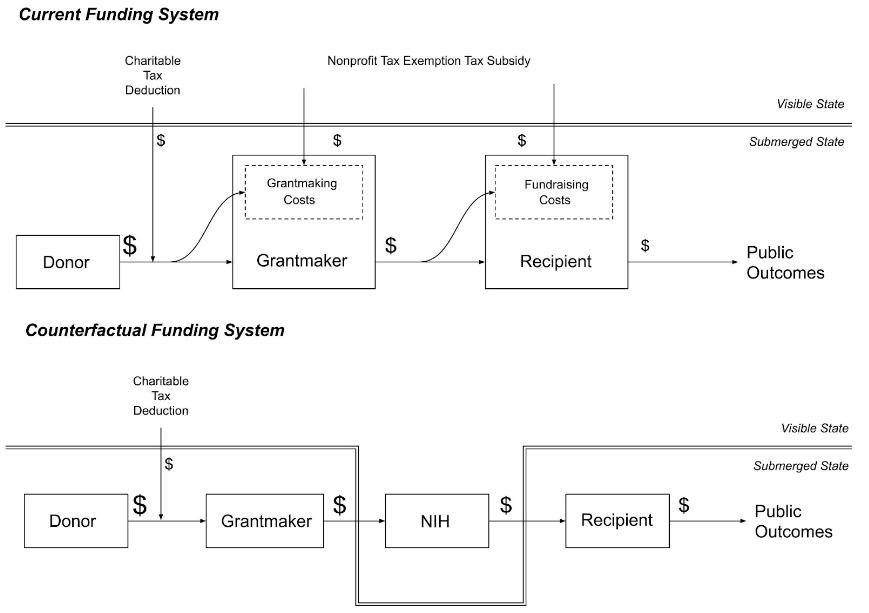
The Inefficiency of Private Support for Public Health:Comparing Nonprofit Biomedical Research Funding with the NIH
Shachter, Simon Y., Donghyun Kang, and James A. Evans, R & R at Research Policy, Preprint
Abstract The U.S. has two systems of funding research at universities—a public one of Congressional appropriations and a private “submerged state” involving nonprofit funders subsidized by taxpayers. Here we examine the case of biomedical research and demonstrate that the “submerged state” can be costly and markedly less efficient at producing public goods. Using disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), we compare published outputs of biomedical research awards from nonprofit funders to grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). We apply a dataset of university funding and create novel linkages between grants and publications addressing diseases. Using this crosswalk, we demonstrate that nonprofit funders inefficiently benefit public health. Publications they fund are associated with fewer DALYs on average and are collectively less representative of the burden of disease than NIH-funded publications. This view implicates the inefficiency of the submerged state in biomedical research for public health, and is consistent with the critique that philanthropic activities represent publicly-sponsored expressions of private good.